- Abemaciclib Intermediates
- Larotrectinib Intermediate
- Ivacaftor Intermediates
- AZD-9574 Intermediate
- AZD-5305 Intermediate
- Delafloxacin Intermediates
- Ponatinib Intermediates
- Baloxavir Intermediates
- Lisapram Intermediates
- Suzetrigine(VX548) Intermediate
- Resmetirol GL3196 Intermediate
- Dotinod Intermediates
- Other Intermediates
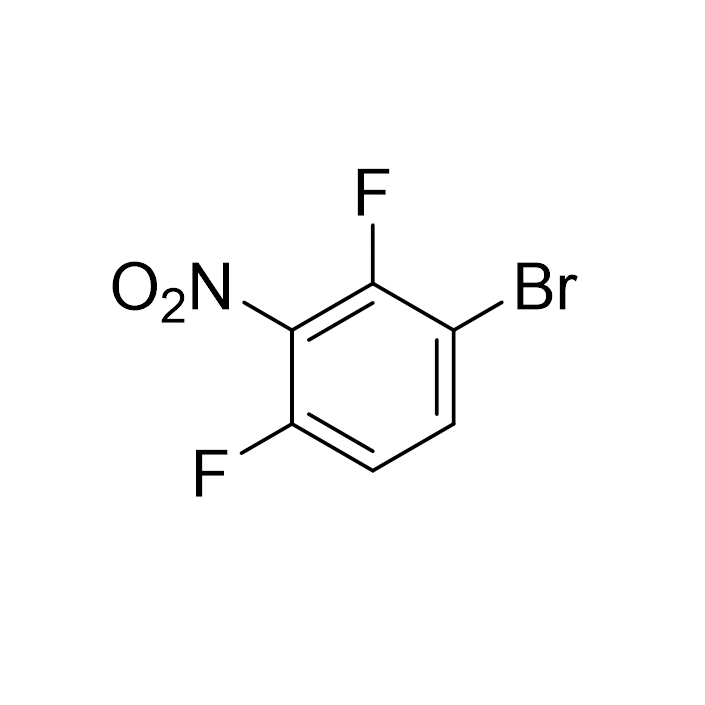
1-BroMo-2,4-difluoro-3-nitrobenzene CAS:1420800-30-1
ZhonghanProduct Overview
1. Basic information: 1-Bromo-2,4-difluoro-3-nitrobenzene and 2,6-difluoro-3-bromonitrobenzene are the same substance, with the English name 1-Bromo-2,4-difluoro-3-nitrobenzene. It has a unique chemical structure, its CAS number is [specific CAS number], its molecular formula is C₆H₂BrF₂NO₂, its molecular weight is 252.0, its exact mass is about 250.92000, and its appearance is mostly light yellow to yellow transparent liquid.
2. Physical and chemical properties: The density is usually [X] g/mL (25°C), with a clear boiling point of about [X]°C and a flash point of about [X]°C. In terms of solubility, it is almost insoluble in water, but can be well miscible with organic solvents such as toluene and chloroform. This property plays a key role in many chemical processes.
3. Synthesis route: Laboratory synthesis often uses 2,4-difluoroaniline as the starting material, first using mixed acid for nitration reaction to successfully introduce nitro group, then converting amino group into diazonium salt through diazotization reaction, and then using Sandmeyer reaction to complete the substitution of bromine atom under the action of reagents such as cuprous bromide. In industrial production, in order to increase output and reduce costs, the reaction conditions will be optimized, continuous production process will be adopted, and factors such as reaction temperature, material ratio and reaction time will be strictly controlled.
ZhonghanStructural formula
Molecular formula |
C6H2BrF2NO2 |
Molecular weight |
237.99 |
Boiling point |
260.8±35.0 °C (Predicted) |
Density |
1.890±0.06 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
Form |
Liquid |
Color |
Clear, light lime/lemon flavor |
ZhonghanPhysical properties
Appearance: Usually pale yellow to yellow liquid.
Smell: It has a distinctive chemical smell, but the specific smell is difficult to describe accurately and may vary slightly due to factors such as purity.
Density: Density is generally around 1.90 g/mL (25°C), which is greater than the density of water. If it is insoluble in water, it will sink to the bottom.
Melting point: There is no very accurate single value reported yet, but it is roughly within a certain low temperature range. The fact that it is liquid at room temperature indicates that its melting point is below 25°C.
Boiling point: The boiling point is about 220 - 230°C, at which the substance changes from liquid to gas.
Flash point: The flash point is about 90 - 100℃, which means that near this temperature, the vapor emitted by it may burn instantly when mixed with air and encounter a fire source.
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in common organic solvents such as toluene, chloroform, dichloromethane, ether, etc. It can be miscible with these organic solvents in a certain proportion to form a uniform solution system.
Refractive index: The refractive index is generally between 1.540 - 1.560 (20°C). This physical property is important for the identification and analysis of the compound by optical methods.
ZhonghanApplication Areas
Medical field
Synthetic antibacterial drugs: The special structure of this compound enables it to participate in the synthesis of antibacterial drugs as a key intermediate. The fluorine atoms and nitro groups it contains can enhance the binding ability of drug molecules to bacterial targets, thereby improving antibacterial activity. For example, in the research and development of some new quinolone antibacterial drugs, it can introduce specific functional groups and optimize the chemical structure of the drug, so that it can also have a better inhibitory effect on drug-resistant bacteria.
Research and development of nervous system drugs: In the design of nervous system drugs, it can be used to construct molecular skeletons with specific pharmacological activities. Fluorine- and nitro-containing structures help drug molecules pass through the blood-brain barrier, bind to receptors in the nervous system, regulate the release and transmission of neurotransmitters, and thus treat nervous system diseases such as epilepsy and depression.
Pesticide field
Preparation of insecticides: It can be used to synthesize new insecticides. Its unique chemical properties can interfere with the nervous system and physiological metabolic processes of insects. For example, some insecticides it participates in synthesizing can act on the ion channels of insects, destroy their nerve conduction, and cause insect paralysis and death. Due to its structural characteristics, it has relatively little impact on the environment, which is in line with the development trend of green pesticides.
Development of fungicides: In the research and development of fungicides, this compound can be used as a precursor of active ingredients. It can destroy the growth and reproduction of fungi by binding to specific targets on the fungal cell wall or cell membrane, and has a good control effect on fungal diseases of various crops, thereby improving the yield and quality of crops.
Materials Science
Synthesis of high-performance polymers: As a monomer or reaction intermediate, it can participate in the synthesis of high-performance polymers. The introduction of fluorine atoms can give the polymer good chemical corrosion resistance, low surface energy and hydrophobicity; nitro groups can improve the heat resistance and mechanical properties of polymers. These polymers can be used to manufacture parts in the aerospace field, insulation materials for electronic equipment, etc.
Preparation of organic optoelectronic materials: In the preparation of organic optoelectronic materials, its structural characteristics enable it to adjust the electronic energy level and optical properties of the material. For example, its application in the synthesis of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) materials can improve the luminous efficiency and stability of the material and promote the development of display technology.
Dye field
In the synthesis of dyes, it can be used as a raw material to introduce specific functional groups, change the structure of dye molecules and the distribution of electron clouds, thereby adjusting the color, dyeing properties, and fastness to light and washing. It is used to synthesize dyes with special color and performance requirements to meet the needs of the textile, printing and other industries.

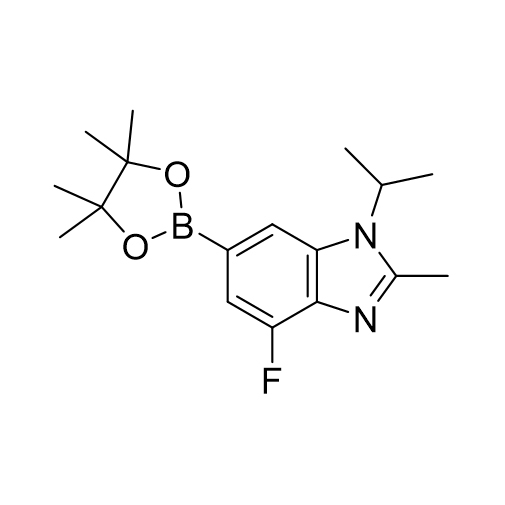
![6-Bromo-4-fluoro-1-isopropyl-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole CAS:1231930-33-8](/source/9e9faa51f944bc7ac934c145f661fec3/cas1231930-33-8.jpg)
![5-Hydroxypyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine CAS:29274-22-4](https://ecdn6.globalso.com/upload/p/3069/image_product/2025-02/cas29274-22-4.jpg)
![5-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine CAS:29274-24-6](/source/2d2e4c8649a6444c8114fbceac0e361d/cas29274-24-6.jpg)
![5-Chloro-3-nitropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyriMidine CAS:1363380-51-1](/source/c735e97d9d2434baa533916048357d17/cas1363380-51-1.jpg)