Leave Your Message
In recent years, the importance of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) in polymer applications has garnered significant attention within the chemical engineering community. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in polymer chemistry, states, “Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride is a versatile building block that enhances the performance characteristics of various polymers.” This highlights the profound impact TBPA can have on improving the properties and functionalities of polymer materials.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for fire retardancy and mechanical performance, Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride offers a unique avenue for achieving these objectives. Its ability to act as an effective flame retardant while also contributing to the structural integrity of polymers makes it an essential component in the development of safer and more durable products. The integration of TBPA into polymer formulations not only meets safety regulations but also supports the growing demand for sustainable materials in diverse applications.
Navigating the challenges of incorporating Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride into polymer systems requires a deep understanding of its chemical behavior and interactions with other components. This article will explore practical methodologies for effectively utilizing TBPA, alongside insights from experts in the field, establishing a comprehensive guide for manufacturers aiming to optimize their polymer applications with this dynamic compound.

Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of flame-retardant polymers. This compound is increasingly utilized in various applications, particularly in electrical and electronic materials, where heat resistance and fire safety are of paramount importance. According to industry reports, the demand for flame-retardant materials is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through the end of the decade, highlighting the significance of additives like TBPA in meeting safety regulations and consumer expectations.
In polymer formulations, TBPA is utilized to enhance thermal stability and reduce flammability without compromising mechanical properties. Its incorporation into resins, such as epoxy and unsaturated polyesters, not only improves fire resistance but also contributes to the overall performance of the material in demanding environments. Additionally, studies indicate that using TBPA can lower peak heat release rates significantly, thus providing an essential safety profile in applications ranging from construction to automotive components. This aligns with the growing trend of sustainable materials, as TBPA enables manufacturers to create compliant products that meet European Union standards and other global fire safety regulations.
Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) is a halogenated compound with a distinct chemical structure that plays a significant role in various polymer applications. Its molecular formula, C8Br4O3, indicates that the compound contains four bromine atoms attached to the phthalic anhydride framework. This unique structure not only influences its thermal and chemical stability but also enhances its effectiveness as a flame retardant in polymer materials. The presence of bromine contributes to TBPA's properties that enable polymers to withstand higher temperatures and resist combustion, making it an essential additive in the production of safer, more efficient materials.
From a chemical perspective, TBPA exhibits a reactivity profile typical of phthalic anhydrides, allowing it to easily undergo esterification and polymerization reactions. The anhydride functional group in TBPA enables it to react with various alcohols and amines, leading to the formation of copolymer structures that can improve the mechanical and thermal properties of the resulting materials. Additionally, the bromine atoms in the molecule can interact with other additives or modifiers in polymer formulations, providing enhanced performance characteristics. This versatility makes TBPA a valuable component in the development of high-performance polymers, particularly in industries where flame resistance and durability are paramount.
This bar chart illustrates the performance metrics of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride in various polymer applications, highlighting key attributes such as thermal stability, flame retardancy, and mechanical properties. Each metric is assessed on a scale of 1 to 100, indicating the effectiveness of Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride in enhancing these polymer characteristics.
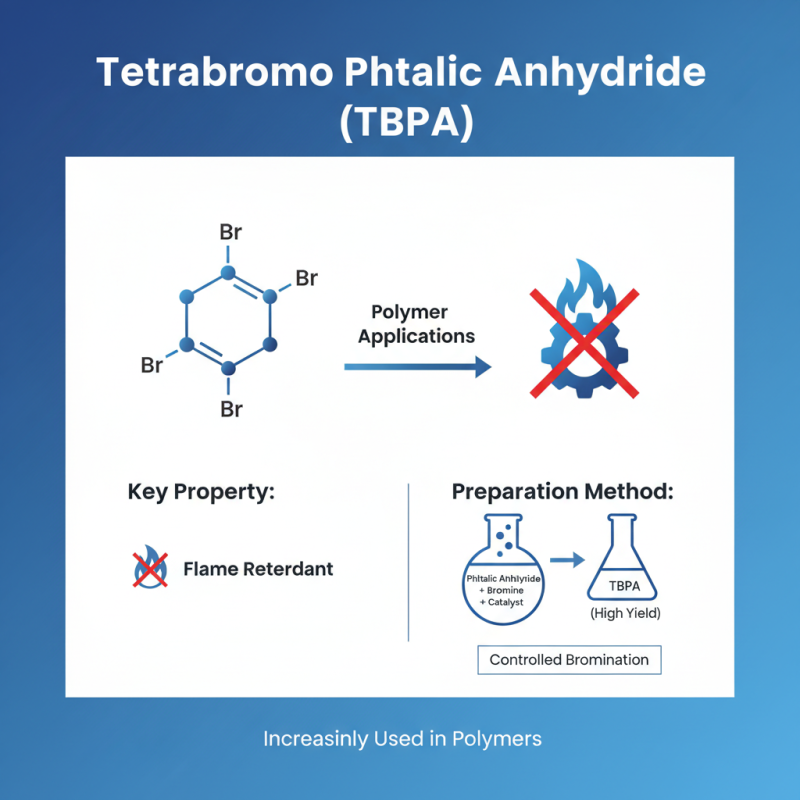
Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride (TBPA) is increasingly utilized in polymer applications due to its flame-retardant properties. The preparation methods for TBPA typically involve the bromination of phthalic anhydride, and several routes can achieve this end. One common method includes the reaction of phthalic anhydride with bromine in the presence of a suitable catalyst. This process allows for controlled bromination, resulting in high yields of TBPA.
Another approach is through the use of liquid-phase bromination, where phthalic anhydride is mixed with bromine in a solvent at elevated temperatures. This method can enhance the reaction rate and obtain purer products, but careful temperature control is essential to prevent unwanted side reactions. Additionally, a modern method involves the use of microwave irradiation, which can significantly reduce reaction time and improve energy efficiency, making it a viable option for large-scale production.
Tips: When preparing TBPA, always ensure that appropriate safety measures are in place, as bromination reactions can be highly exothermic. Utilizing personal protective equipment and conducting reactions in a fume hood can help mitigate risks. Furthermore, pay close attention to stoichiometric ratios to optimize yield and minimize by-products during the synthesis process.

Tetrabromo phthalic anhydride (TBPA) plays a crucial role in various polymer chemistry applications due to its unique chemical properties. One of the primary uses of TBPA is as a flame retardant additive in thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers. Its high bromine content effectively reduces the flammability of materials, making it an ideal component for producing safer consumer goods, electronics, and automotive parts. By incorporating TBPA, manufacturers can enhance the thermal stability of resins, thereby improving the performance and safety of the final products.
Another significant application of TBPA in polymer chemistry is its capacity to function as a curing agent in the synthesis of epoxy resins. When utilized in epoxy formulations, TBPA enhances crosslinking density, contributing to the overall mechanical strength and durability of the material. This property is particularly valuable in industries such as construction and aerospace, where high-performance materials are required to withstand extreme conditions. As research continues to advance the understanding of TBPA's interactions within polymer matrices, there is potential for exploring additional innovative applications in composite materials and coatings.
Tetrabromo phthalic anhydride (TBPA) is increasingly utilized in polymer applications due to its flame-retardant properties. However, safety and environmental considerations must be a priority when working with this chemical. According to industry reports, TBPA can pose potential health risks, including skin and eye irritation, and inhalation can lead to respiratory issues. Thus, ensuring proper ventilation and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and masks is crucial during its handling.
Moreover, the environmental impact of TBPA cannot be overlooked. This compound has been flagged due to its persistence in the environment and potential bioaccumulation in aquatic systems. It's critical to adhere to waste disposal regulations and consider substituting TBPA with safer alternatives whenever possible. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggests incorporating risk assessments before use to mitigate adverse effects on ecosystems.
**Tips for Safe Usage:**
1. Always conduct a thorough risk assessment and utilize appropriate containment measures to prevent accidental spills.
2. Leverage safety data sheets (SDS) to stay informed on the proper handling and emergency response protocols associated with TBPA.
3. Encourage regular training sessions for employees to raise awareness about safe practices and environmental responsibilities when working with hazardous materials like TBPA.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Tetrabromo Phthalic Anhydride |
| CAS Number | 32588-76-4 |
| Application | Flame retardant in polymers |
| Safety Precautions | Use personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves and masks |
| Environmental Impact | Potential hazard to aquatic life; should be managed properly |
| Regulatory Status | Complies with REACH regulations; monitoring of use is recommended |
| Safe Disposal Methods | Follow local regulations; incineration recommended over landfill |






